Deploying a Scalable and Secure Three-Tier Architecture on AWS
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Network Architecture Diagram
- Understanding the Three Tiers
- Essential AWS Services
- Step-by-Step Deployment
- Step 1: Download the Project Code
- Step 2: Create an S3 Bucket for Static Content
- Step 3: Set Up an IAM Role for EC2
- Step 4: Configure a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Step 5: Set Up Internet and NAT Gateways
- Step 6: Configure Route Tables
- Step 7: Launch EC2 Instances
- Step 8: Set Up RDS (Database Layer)
- Step 9: Configure Security Groups
- Best Practices for Optimization
- Conclusion
Introduction
A three-tier architecture is a structured approach to cloud infrastructure, ensuring scalability, security, and high availability. It consists of:
Presentation Layer (Web Tier) – Handles incoming requests (EC2 in Public Subnet).
Application Layer (Business Logic Tier) – Processes backend logic (EC2 in Private Subnet).
Database Layer (Data Tier) – Stores and manages application data securely (RDS in Private Subnet).
In this guide, we’ll go through each step of setting up a three-tier web application using AWS services, focusing on networking, load balancing, and database management.
Network Architecture Diagram

Understanding the Three Tiers
1. Web Layer (Presentation)
Manages user interactions and forwards requests to the application layer.
Hosted on EC2 instances in public subnets.
Uses Application Load Balancer (ALB) for traffic distribution.
Implements AWS CloudFront for caching static content.
Secured using AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF).
2. Application Layer (Business Logic)
Processes requests and handles backend logic.
Hosted on private EC2 instances.
Uses Internal ALB for request routing.
Deploys PHP with Apache on Amazon Linux 2.
API integration using Amazon API Gateway.
3. Database Layer (Storage)
Stores and manages data securely.
Uses Amazon RDS (MySQL) in private subnets.
Configured for Multi-AZ replication for high availability.
Read replicas enabled for handling high-load queries.
Automated backups and snapshots for disaster recovery.
Essential AWS Services
1. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Provides isolated network for resources.
Divided into public and private subnets.
Connects to the internet via Internet Gateway (IGW).
Uses NAT Gateway for outbound traffic from private subnets.
2. Application Load Balancer (ALB)
Distributes traffic across EC2 instances.
Public ALB routes traffic to web servers.
Internal ALB handles app layer communication.
Supports SSL termination for secure connections.
3. Amazon EC2 Instances
Web tier runs in public subnets.
Application tier hosted in private subnets.
Uses Auto Scaling for elasticity.
Runs PHP with Apache on Amazon Linux 2.
4. Amazon RDS (MySQL)
Fully managed database service.
Multi-AZ deployment for high availability.
IAM authentication for secure access.
Performance Insights for monitoring.
5. IAM & Security Configurations
IAM roles grant AWS service permissions.
Security Groups control network access.
AWS WAF protects against common threats.
AWS Secrets Manager secures credentials.
Step-by-Step Deployment
Step 1: Download the Project Code
Begin by cloning the necessary project repository from GitHub to have access to the required codebase.
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-three-tier-web-architecture-workshop.git
Step 2: Create an S3 Bucket for Static Content
Navigate to AWS Management Console > S3.
Click "Create bucket" and provide a unique name.
Select a region close to your users.
Enable Block Public Access (unless the bucket needs to serve static content publicly).
Click "Create bucket".

Step 3: Set Up an IAM Role for EC2
Go to AWS Management Console > IAM > Roles.
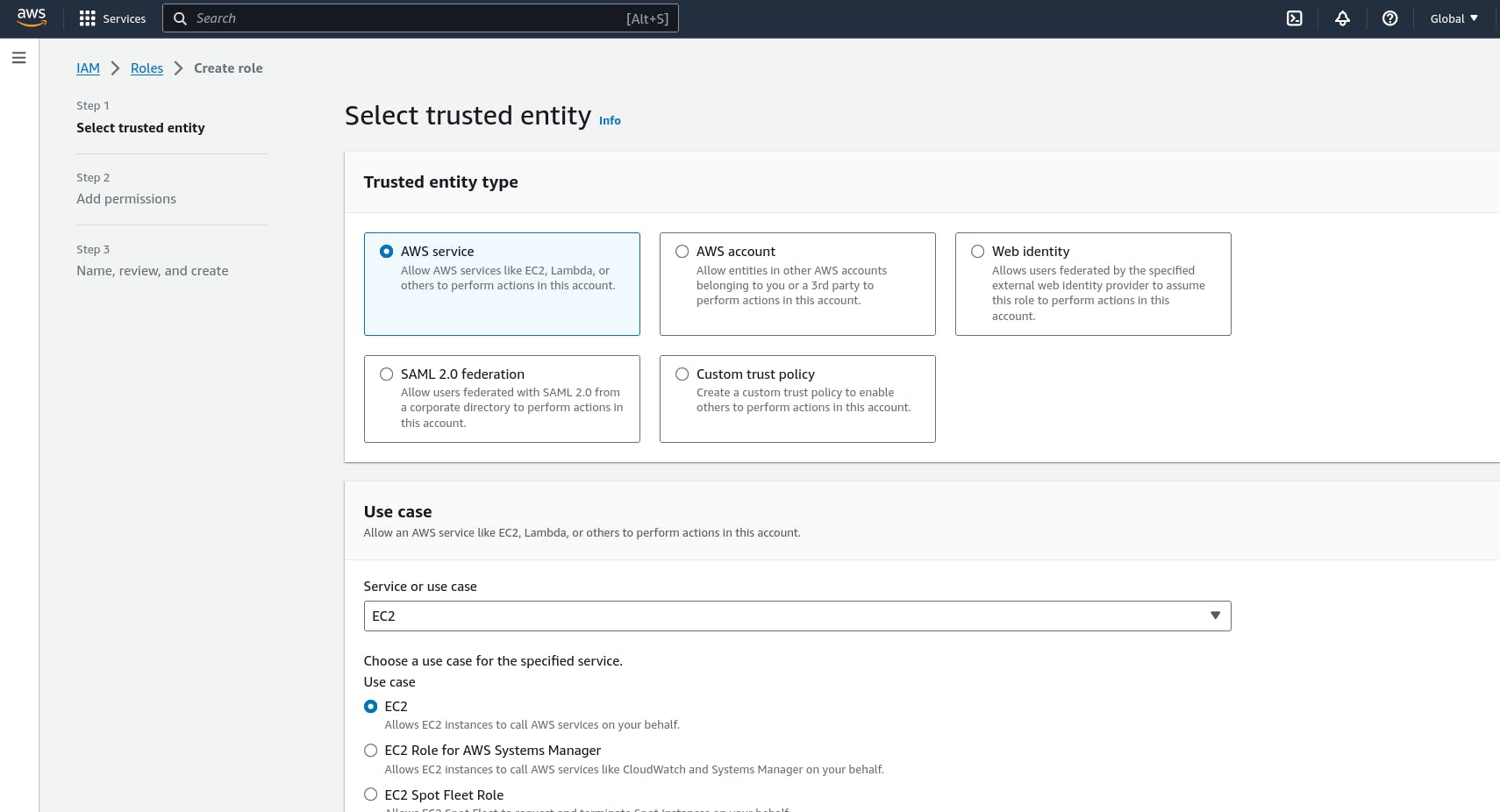
Click "Create role" and select EC2 as the trusted entity.
Attach the following policies:
AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess(for accessing S3).AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore(for AWS Systems Manager).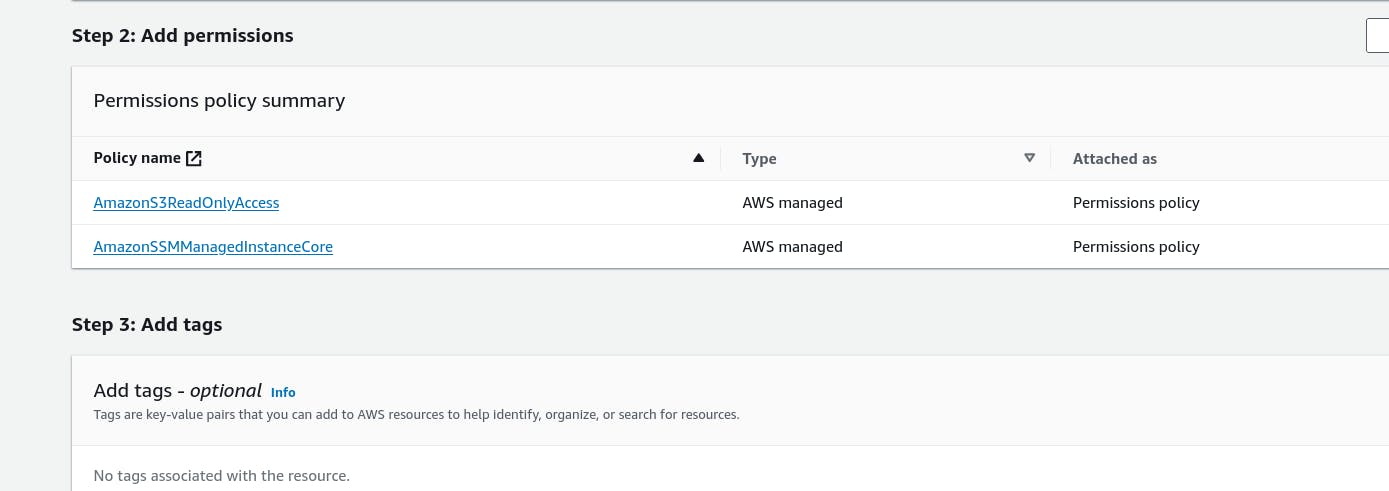
Name the role and create it.
Assign this role to your EC2 instances later.
Step 4: Configure a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Go to VPC > Subnets > Create subnet.

Create the following subnets:
Two Public Subnets (for the Web Tier, e.g., 10.0.1.0/24, 10.0.2.0/24).
Two Private Subnets (for the Application Tier, e.g., 10.0.3.0/24, 10.0.4.0/24).
Two Private Subnets (for the Database Tier, e.g., 10.0.5.0/24, 10.0.6.0/24).

Associate subnets with the VPC.

Step 5: Set Up Internet and NAT Gateways
Go to VPC > Internet Gateways and create an Internet Gateway.

Attach it to your VPC.

In VPC > NAT Gateways, create a NAT Gateway in the public subnet.
Assign an Elastic IP to the NAT Gateway.

Step 6: Configure Route Tables
Go to VPC > Route Tables.
Create:
A Public Route Table and add a route for
0.0.0.0/0via the Internet Gateway.A Private Route Table and add a route for
0.0.0.0/0via the NAT Gateway.




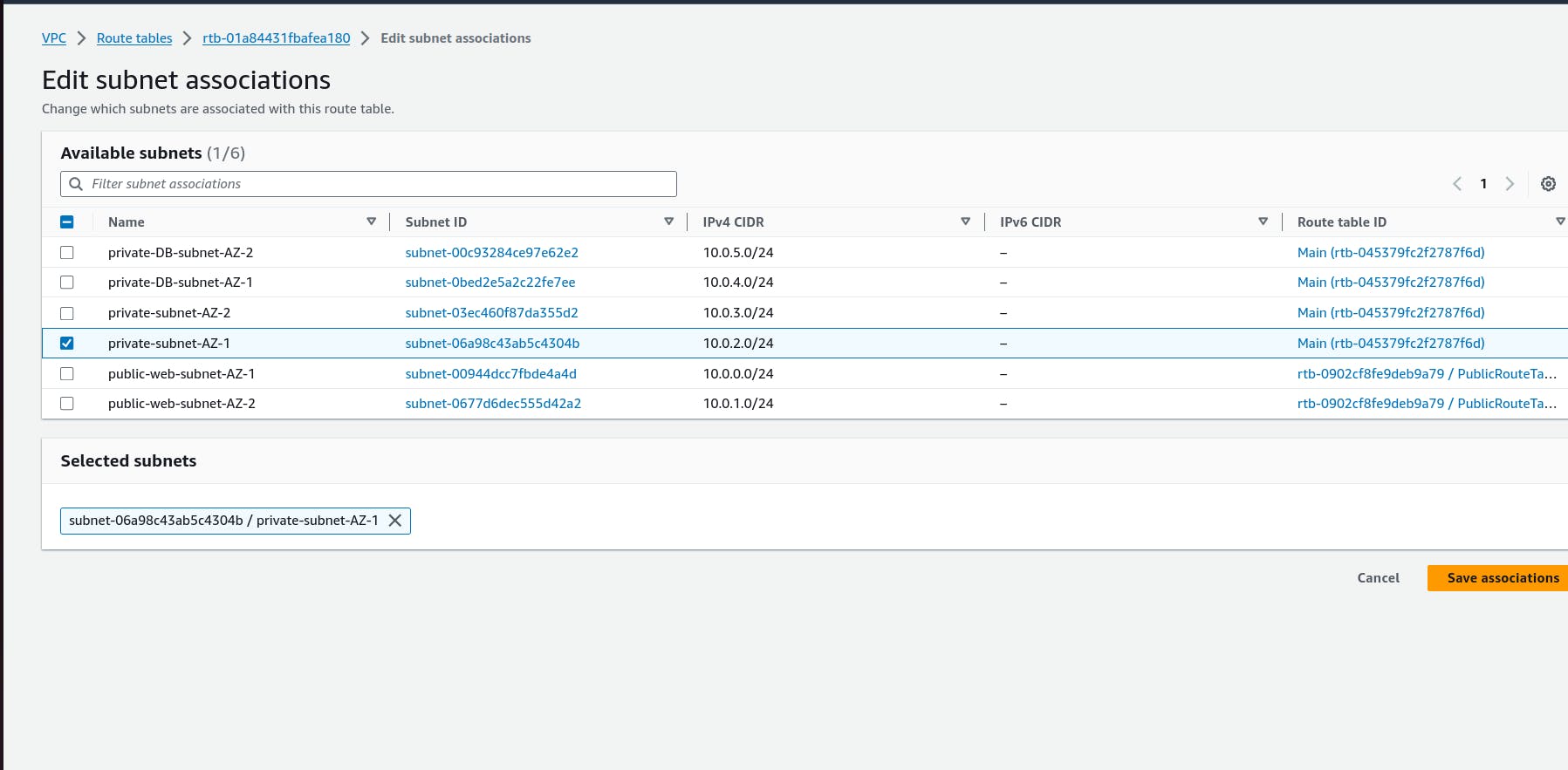
Associate the public subnets with the Public Route Table.
Associate the private subnets with the Private Route Table.
Step 7: Launch EC2 Instances
Web Layer (Frontend):
Navigate to EC2 > Launch Instance.

Choose Amazon Linux 2 or Ubuntu.
Attach the IAM Role created earlier.
Assign a key pair for SSH access.
Place the instance in a public subnet.
Install a web server:
bashCopyEditsudo yum update -y
sudo yum install httpd -y
sudo systemctl start httpd
sudo systemctl enable httpd
Application Layer (Backend):
Launch another EC2 instance for the backend in a private subnet.
Assign the IAM Role.
Install required backend services.
Step 8: Set Up RDS (Database Layer)
Navigate to RDS > Create Database.

Select MySQL or PostgreSQL.

Enable Multi-AZ Deployment for high availability.

Place the database in a private subnet.
Create a database security group to allow traffic only from the application layer


Step 9: Configure Security Groups
Web Layer Security Group:
Allow HTTP (80), HTTPS (443), and SSH (22) from your IP.


Application Layer Security Group:
Allow traffic only from the Web Layer Security Group on the backend port (e.g., 8080).


Database Layer Security Group:
- Allow traffic only from the Application Layer Security Group on port 3306 (MySQL) or 5432 (PostgreSQL).

Best Practices for Optimization
Scalability:
- Utilize Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancers to ensure your architecture handles increased traffic.
Security:
- Enable IAM roles, VPC security groups, and AWS WAF for added protection against threats.
Monitoring:
- Leverage AWS CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and VPC Flow Logs for comprehensive monitoring and logging.
Cost Management:
- Consider AWS Savings Plans and Spot Instances to optimize costs and ensure efficient resource use.
Conclusion
A well-structured three-tier architecture on AWS provides a robust foundation for modern cloud applications, ensuring optimal performance, security, and scalability. Utilizing services like VPC, EC2, RDS, ALB, IAM, and CloudFront enables organizations to build an efficient and cost-effective infrastructure that meets dynamic business needs.
This deployment model enhances system reliability, streamlines resource management, and strengthens security, making it a preferred choice for cloud-based applications.